Coronavirus Covid-19: Sectors that are down and those that are growing
Since March 17, 2020 at 12:00 am, France has been in confinement. The decision was taken by the President of the Republic, Emmanuel MACRON, during his address to the French people the evening before for health reasons, in response to the Covid-19 pandemic. Before the explosion of the pandemic in the United States, Europe was considered the epicentre of the health crisis that emerged in the city of Wuhan, China.
Within the framework of European coordination under the aegis of the European Commission on 16 March 2020, most European countries have also adopted this measure to varying degrees.
In this article, we will discuss the following topics:
✅ The impact on the economy in France and Europe
✅ The sectors that have broken down and those that are growing
✅ Opportunities for Interim Managers
✅ Operational and available solutions for companies
✅ French economy: impacts and consequences of the Covid-19 coronavirus
As at 30 March 2020, the latest OFCE impact study predicts a cost to the French economy of slightly more than 30 points of monthly GDP per month to confirm. This represents a loss of 2.6% of annual GDP, i.e. a loss of 60 billion euros per month of containment.
On a cumulative basis and as at 20 April 2020, the latest estimates by the French government show a decline of 8% in GDP, forecast for the year 2020. The debt is expected to reach 115% of GDP, compared to 99% in the initial budget for the current year.
What leads to this phenomenal drop in GDP? The fall in household consumption, estimated at 18% according to the OFCE, the drop in investment and the confinement of the workforce. In addition, the impact of this crisis on tourism could lead to a loss of 14 billion euros per month. This is due to the containment and closure of borders.
This unprecedented situation makes it very difficult for companies to continue their activities. Many have been forced to close and shut down their operations due to government decisions. Others are facing labour shortages for various reasons: sick employees, parental leave or exercising the right of withdrawal for health reasons, all of which have a strong impact on GDP and the production of national wealth.
✅ European economy: impacts and consequences of the Covid-19 coronavirus
In order to respond to this exceptional situation, the European Commission has taken supportive measures in the health and economic fields. Ursula von der LEYEN, President of the European Commission, announced a new draft European budget for the financial year 2021-2027.
In the spirit of a European “Marshall Plan”, this project will include “a recovery plan that will ensure that cohesion within the Union is maintained through solidarity and responsibility”, the President said. This budget is announced as being “at the heart” of the measures put in place to stem the pandemic.
Although the full details of the project are not yet known, the Commission promises not to “exclude any option authorised within the limits of the Treaty” in order to get out of this critical situation, according to the newspaper Politico.
After failing to reach an agreement among the 27 EU countries at the European Council, finance ministers reached a €540 billion recovery deal at a meeting on 9 April 2020. The plan has three pillars: the European Stability Mechanism (ESM) for €240 billion, the European Investment Bank (EIB) for €200 billion and the “Sure” plan for €100 billion to benefit the partially unemployed in the European Union.
(Source: touteleurope.eu and les Echos)
✅ Sectors in breakdown due to the Covid-19 coronavirus
The vast majority of companies will suffer or have economic consequences related to this health crisis.
On the stock market, the Covid-19 crisis first affected stocks that are closely linked to Chinese consumption. Stocks in the luxury sector such as Kering or LVMH, air transport or tourism (Air France-KLM, Accor) saw red. Groups that own factories in the Wuhan region (epicenter of the epidemic), like Seb or PSA, also saw their value sanctioned by the markets. Overall, the CAC 40 index thus went from more than 6,100 points on 19 February 2020 to 4,520 on 20 April 2020, i.e. a loss of 26% in 3 months after reaching a low of 3,750 points on 18 March 2020 (-38%).
From a sectoral point of view, below is a summary diagram of the economic sectors most affected in France (source: McKinsey).
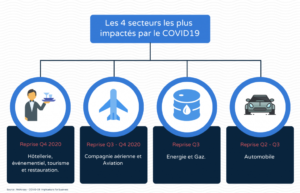
For the aeronautics sector: the Air France group’s shares have lost 50% of their value, and those of Aéroport de Paris have undergone the same evolution. The airlines Easy-Jet and Ryanair, currently have no more planes in flight. The Air France – KLM Group only handles about 10% of its business, mainly through cargo and repatriation flights at the request of the French and Dutch governments.
In the oil sector, which was very buoyant before the crisis, oil prices fell by -65% between February and mid-April 2020. This is due to the combined effect of falling demand and a disagreement between producers over quotas. Oil exploration and drilling companies have given up the search for new deposits and the para-oil sector is going through an unprecedented crisis. Several French companies are directly affected, such as Technip FMC and Vallourec, which have announced cuts in investment and major cost-cutting measures.
Among the other sectors, the most affected remain tourism, hotels and restaurants. Containment measures are thus depriving these professionals of their customers. To date, initial estimates speak of a loss of 40 billion euros for French tourism in 2020 alone.
✅ Growth sectors following the Covid-19 coronavirus
Conversely, some sectors are managing to limit the impact of the pandemic and even develop new opportunities.
Large-scale distribution and local shops, which are still in business, are not suffering from the situation. The Carrefour group and Casino, for example, are the stocks that have changed the least since the beginning of the crisis.
The majority of technology and media companies have managed to make the transition to telework within a few days. For example, the Microsoft Teams service (VoIP, videoconferencing) increased its subscriber base by 12 million in March 2020 and has 44 million daily users.
These sectors are therefore not, or only slightly, impacted by the containment measures and the resulting short-time working measures. A study by the DARES (statistical department of the Ministry of Labour) indicates that less than 13% of short-time work requests come from specialised, scientific and technical service activities. In total, however, more than 9.6 million employees in France are affected by these measures (Source, Ministry of Labour and statement by Minister Muriel Pénicaud of 20 April 2020).
Of course, the e-commerce and home delivery services sectors are growing strongly, and most are doing well during this crisis. Home delivery services have also begun to transition their logistics supply chains to compensate for the loss of their traditional suppliers (restaurants). Combined with mass distribution, they now allow direct delivery of groceries to homes or “contactless” drives.
This is where companies must innovate to direct their efforts in the face of this unprecedented situation: transforming a problem into an opportunity, so that they do not have to face a widespread recession.

The 2019 Work-Sharing Barometer produced by “The Work-Sharing Portal” also allows us to make some interesting observations. According to this study, 93% of people practicing job sharing (*) are satisfied with it. Currently, 430,000 professionals are already working under this procedure in France.
(*) Activity enabling a professional to work for several companies in parallel and, for the latter, to share his skills and time as required.
This Covid-19 coronavirus crisis we are going through shows us that it is possible and necessary to reinvent one’s organization. In order to do so, a certain number of changes are necessary to organise professional life in “confinement” mode and the implementation of remote management.
In order to best organize this new issue, many companies are calling on interim managers to assist them, even during this period. Their role will then be to facilitate the work of each of the organisations’ core businesses by providing experienced and operational support.
This crisis support, to which a large number of interim managers are accustomed, makes it possible to compensate for temporary skills shortages within companies. It will be all the more relevant and effective if the interim manager is not himself isolated but also supported by a trusted network of experts and references.

✅ Opportunities for Interim Managers
✅ Operational and available solutions for companies
As we can therefore see, the current situation offers us the opportunity to deeply question our ways of operating. Firstly, with regard to our companies and organisations. The distance imposed by the virus makes it easier to implement new management. Peer-to-peer exchanges, according to each person’s role and not only according to their position in the pre-confinement hierarchy.
Paradoxically, this facilitates the interaction between professionals and employees within companies.
The FIT in NETWORK® network based on a community of more than 800 experts has developed for several years according to this collaborative model and continues to accompany its clients in this Covid-19 coronavirus situation. On the platform are experts with more than 15 years of professional experience in Management, Finance and Human Resources in all sectors of the economy, able to intervene throughout France and Europe.
Their availability, sector experience, skills and examples of missions already carried out are directly accessible and the pre-selection criteria made available enable companies to identify them quickly. Beyond that and to facilitate your search for solutions, the FIT in NETWORK® teams remain operational, mobilized and united in this phase of Covid-19 to help companies to manage this unprecedented situation.
Bruno d’ARTAGNAN
President of FIT in NETWORK®.
www.fitin-network.com
You are a company and would like to use interim management?
Contact us at +33 1 53 89 09 79 or by email at contact@fitin-network.com.
We will do our utmost to meet your expectations!
FIT in NETWORK®’s commitments to its customers :
-
From the confirmation of an assignment: 3 proposals of candidates in one week;
-
The final choice of the interim manager left to the client, according to the “best FIT”;
-
The follow-up during the mission, at a minimum monthly rhythm, with the client and the interim manager;
-
In case of unavailability of the interim manger, the replacement of the expert on mission within a week;
-
The continuous adaptation of the mission to the client’s particular context.
